Home > Press > Liquid Crystal Design: Engineers develop technique to craft new materials using liquid crystals as structural guides
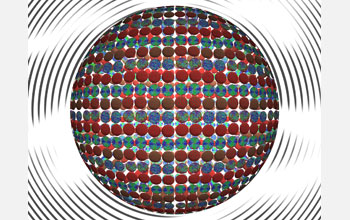 |
| In this creative illustration, each small disc depicts actual data from computational models of nanometer-scale droplets containing liquid crystals, water and surfactants (molecules that lower the surface tensions of liquids). The different patterns show how the surfactants self-organize as they interact with liquid crystals on each droplet's surface.
Credit: Juan de Pablo, University of Wisconsin - Madison |
Abstract:
Liquid crystals, ubiquitous in cell-phone screens and computer monitors, were known to science long before engineers realized their utility in displays and other technologies. Now, an international team of researchers has discovered how to use liquid crystals as scaffolding to build novel materials with undiscovered properties.
Liquid Crystal Design: Engineers develop technique to craft new materials using liquid crystals as structural guides
Arlington, VA | Posted on May 3rd, 2012Reporting their findings in the journal Nature on May 3, the researchers describe a sophisticated computational model for determining how liquid crystals behave within the confines of nanometer-scale droplets containing molecules that lower the surface tensions of liquids, called surfactants.
The researchers, led by University of Wisconsin-Madison engineer Juan de Pablo, show that as the droplets cool, the liquid crystals confine the surfactant molecules, organizing them into discrete structures.
As the researchers adjusted the model's parameters, such as droplet size or surfactant concentration, the simulation revealed that it is possible to use the technique to guide self-assembled structures with a wide range of properties and applications.
For example, the researchers suggest the technique could be used to construct materials from DNA building blocks, allowing unique detectors for biological materials and toxins.
"The researchers have taken a new and exciting approach to the study of liquid crystals, which will have impact in several scientific and technical arenas," adds Mary Galvin, National Science Foundation (NSF) program director for Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers.
NSF supported the research through the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Center on Nanostructured Interfaces, an NSF Center of Excellence for Materials Research and Innovation.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2012, its budget is $7.0 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and other institutions. Each year, NSF receives over 50,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes about 11,000 new funding awards. NSF also awards nearly $420 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Joshua A. Chamot
NSF
(703) 292-7730
Terry Devitt
Univeristy of Wisconsin - Madison
(608) 262-8282
Program Contacts
Mary E. Galvin
NSF
(703) 292-8562
Principal Investigators
Juan de Pablo
Univeristy of Wisconsin - Madison
(608) 262-7727
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








