Home > Press > Nature notices PKU's new solar battery in carbon nanotubes
 |
Abstract:
Peking University (PKU) Professor Peng Lianmao published Research Efficient Photovoltage Multiplication in Carbon Nanotubes on Nature Photonics (2011, 5, PP.672-676), with PhD candidates from PKU School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science, Yang Leijing and Wang Shengfu, as co-writers.
Nature notices PKU's new solar battery in carbon nanotubes
Beijing, China | Posted on November 24th, 2011Nature Photonics is one of the periodicals belonging to the renowned journal Nature. The research paper contains major breakthrough in the study of nanoelectronic applications. It at the same time represents the new progress in the field of nanoelectronic applications made by Professor Peng Lianmao's team.
With the background that natural resource is more and more meager, solar power has many unsurpassable advantages as an alternative energy source. At present, global researches in solar photovoltage mainly focus on the study of photovoltaic devices based on new nanomaterials.
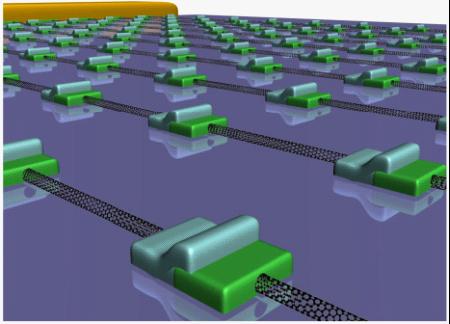
Carbon nanotubes are direct-bandgap materials that are not only useful for nanoelectronic applications, but also have the potential to make a significant impact on the next generation of photovoltaic technology. A semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) has an unusual band structure, as a result of which high-efficiency carrier multiplication effects have been predicted and observed, and films of SWCNTs with absorption close to 100% have been reported. Other important features for photovoltaic applications include high mobility and the availability of ohmic contacts for both electrons and holes. However, the photovoltage generated from a typical semiconducting SWCNT is less than 0.2V, which is too small for most practical photovoltaic applications. Given this background, the researchers successfully showed how this value was readily multiplied by using virtual contacts at the carbon nanotube, which turned to be an important and challenging job.
Professor Peng and his team worked out an approach, the key to which was the introduction of a local virtual contact to the CNT. This contact is virtual in the sense that it is not intended to be connected to the external circuit. In one example, more than 1.0V is generated from a 10-mm-long carbon nanotube with a single-cell photovoltage of 0.2V. This work was realized based on the forward researches conducted by the same team.
In 2008, the research group put forward a method to form carbon nanotube (CNT) diodes using asymmetrically contacts between electrodes. This research finding was published on Advanced Materials (2008, 20, 3258). On this basis, using almost the same but improved methods, the team invented the first carbon tube infrared light-emitting diode (LED), Nano Letters (2011, 11, 23) reported.
The study was supported by the China's National Basic Research Program, and funded by the National Natural Science Fund Committee (NNSFC).
Written by: Jiang Zhaohui
Edited by: Arthars
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Peking University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








