Home > Press > Nano-tech makes medicine greener
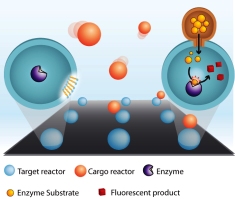 |
| The ultra small nanoreactors have walls made of lipids. During their fusion events volumes of one billionth of a billionth of a liter were transferred between nanoreactors allowing their cargos to mix and react chemically. We typically carried out a million of individual chemical reactions per cm2 in not more than a few minutes. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen are behind the development of a new method that will make it possible to develop drugs faster and greener. This will lead to cheaper medicine for consumers.
Nano-tech makes medicine greener
Copenhagen, Denmark | Posted on November 3rd, 2011Over the last 5 years the Bionano Group at the Nano-Science Center and the Department of Neuroscience and Pharmacology at the University of Copenhagen has been working hard to characterise and test how molecules react, combine together and form larger molecules, which can be used in the development of new medicine.
The researchers' breakthrough, as published in the prestigious journal Nature Nanotechnology, is that they are able to work with reactions that take place in very small volumes, namely 10-19 liters. This is a billion times smaller than anyone has managed to work with before. Even more intriguing is the ability to do so in parallel for millions of samples on a single chip.
"We are the first in the world to demonstrate that it is possible to mix and work with such small amounts of material. When we reach such unprecedented small volumes we can test many more reactions in parallel and that is the basis for the development of new drugs. In addition, we have reduced our use of materials considerably and that is beneficial to both the environment and the pocketbook," says professor Dimitrios Stamou, who predicts that the method will be of interest to industry because it makes it possible to investigate drugs faster, cheaper and greener.
The technique makes production greener
The team of professor Stamou reached such small scales because they are working with self-assembling systems. Self-assembling systems, such as molecules, are biological systems that organise themselves without outside control.
This occurs because some molecules fit with certain other molecules so well that they assemble together into a common structure. Self-assembly is a fundamental principle in nature and occurs at all the different size scales, ranging from the formation of solar systems to the folding of DNA.
"By using nanotechnology we have been able to observe how specific self-assembling systems, such as biomolecules, react to different substances and have used this knowledge to develop the method. The self-assembling systems consist entirely of biological materials such as fat and as a result do not impact the environment, in contrast to the materials commonly used in industry today (e.g. plastics, silicon and metals). This and the dramatic reduction in the amount of used materials makes the technique more environment friendly, ‘greener'," explains Dimitrios Stamou, who is part of the Synthetic Biology Center and director of the Lundbeck Center Biomembranes in Nanomedicine.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nørregade 10, PO box 2177
1017 Copenhagen K
Contact:
News editor
Copyright © University of Copenhagen
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Self Assembly
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








