Home > Press > Packing the ions
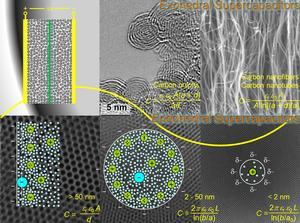 |
| Computational modeling of carbon supercapacitors with the effects of surface curvature included. (Image credit: Jingsong Huang, ORNL) |
Abstract:
Discovery boosts supercapacitor energy storage
Packing the ions
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on June 17th, 2011Flat is in the eye of the beholder.
When you're talking about nanomaterials, however, that eye is pretty much useless unless it's looking through an electron microscope or at a computer visualization. Yet the pits and ridges on a seemingly flat surface—so small they are invisible without such tools—can give the material astonishing abilities. The trick for researchers interested in taking advantage of these abilities lies in understanding and, eventually, predicting how the microscopic topography of a surface can translate into transformative technologies.
Drexel University's Yury Gogotsi and colleagues recently needed an atom's-eye view of a promising supercapacitor material to sort out experimental results that were exciting but appeared illogical. That view was provided by a research team led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) computational chemists Bobby Sumpter and Jingsong Huang and computational physicist Vincent Meunier.
Gogotsi's team discovered you can increase the energy stored in a carbon supercapacitor dramatically by shrinking pores in the material to a seemingly impossible size—seemingly impossible because the pores were smaller than the solvent-covered electric charge-carriers that were supposed to fit within them. The team published its findings in the journal Science.
The mystery was not simply academic. Capacitors are an important technology that provides energy by holding an electrical charge. They have several advantages over traditional batteries—charging and discharging nearly instantaneously and recharging over and over again, almost indefinitely, without wearing out—but they also have drawbacks—most importantly, they hold far less energy.
An electric double-layer capacitor, or supercapacitor, represents an advance on the technology that allows for far greater energy density. While in traditional capacitors two metallic plates are separated by a nonconducting material known as a dielectric, in a supercapacitor an electrolyte is able to form an electric double layer with electrode materials that have very high surface areas.
As such, supercapacitors are able to achieve the same effect within a single material, as properties of the material divide it into separate layers with a very thin, nonconducting boundary. Because they can both forgo a bulky dielectric layer and make use of the carbon's nanoscale pores, supercapacitors are able to store far more energy than their traditional counterparts in a given volume. This technology could help increase the value of energy sources that are clean, but sporadic, meting out stored energy during downtimes such as night for a solar cell or calm days for a wind turbine.
So Gogotsi's discovery was potentially ground breaking. The energy was stored in the form of ions within an electrolyte, with the ions surrounded by shells of solvent molecules and packed on the surfaces of nanoporous carbons. The researchers were able to control the size of pores in the carbon material, making them 0.7 to 2.7 nanometers. What they found was that the energy stored in the material shot up dramatically as the pores became smaller than a nanometer, even though the ions in their solvation shells could not fit into spaces that small.
"It was a mystery," Sumpter said. "Many people questioned the result at the time. Yet the experimental data was showing an incredible increase in capacitance."
Fortunately, it was a mystery that the ORNL team could unravel.
"We thought this was a perfect case for computational modeling because we could certainly simulate nanometer-sized pores," Sumpter said. "We had electronic-structure capabilities that could treat it well, so it was a very good problem for us to explore."
Using ORNL's Jaguar and Eugene supercomputers, Sumpter and his team were able to take a nanoscale look at the interaction between ion and carbon surface. A computational technique known as density functional theory allowed them to show that the phenomenon observed by Gogotsi was far from impossible. In fact, they found that the ion fairly easily pops out of its solvation shell and fits into the nanoscale pore.
"It goes in such a way that it desolvates in the bulk to get inside because there's electrostatic potential and van der Waals forces that pull it in," Sumpter explained. "There are a whole lot of different forces involved, but in fact it's very easy for it to get in."
The ORNL team and colleagues at Clemson University, Drexel University, and Georgia Tech detailed their findings in a series of publications, including Angewandte Chemie, Chemistry-A European Journal, ACS Nano, Journal of Chemical Physics C, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Journal of Materials Research, and Nano Letters.
"In addition," Sumpter noted, "the microscopic bumps and divots on a carbon plate make a dramatic difference in the amount of energy that can be stored on or in it.
"When you get to the nanoscale, the surface area is huge, and the curvature, both concave and convex, can be very large. This makes a large difference in the capacitance. We derived a model that explained all the experimental data. You can back out the pieces of the model from the electronic structure calculations, and from that model you can predict capacitance for different types of curved shapes and pore sizes."
For example, he said, the calculations showed that the charge-carrying ions are stored not only by slipping into pores but also attaching to mounds in the material.
"It's a positive curvature instead of a negative curvature," Sumpter said, "and they can store and release energy even faster. So you can store ions inside a hole or you can store ions outside."
Using these and other insights gained through supercomputer simulation, the ORNL team partnered with colleagues at Rice University to develop a working supercapacitor that uses atom-thick sheets of carbon materials.
"It uses graphene on a substrate and a polymer-gel electrolyte," Sumpter explained, "so that you produce a device that is fully transparent and flexible. You can wrap it around your finger, but it's still an energy storage device. So we've gone all the way from modeling electrons to making a functional device that you can hold in your hand."— Leo Williams, June 16, 2011
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
P.O. Box 2008
Oak Ridge, TN 37831
(+1) 865.574.4160
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Drexel University's Yury Gogotsi
Drexel University's Yury Gogotsi
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








