Home > Press > Quantum sensor tracked in human cells could aid drug discovery
 |
Abstract:
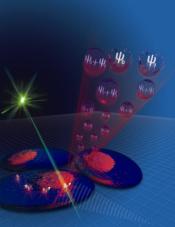
Groundbreaking research has shown a quantum atom has been tracked inside a living human cell and may lead to improvements in the testing and development of new drugs.
Quantum sensor tracked in human cells could aid drug discovery
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on May 26th, 2011Professor Lloyd Hollenberg from the University of Melbourne's School of Physics who led the research said it is the first time a single atom encased in nanodiamond has been used as a sensor to explore the nanoscale environment inside a living human cell.
"It is exciting to see how the atom experiences the biological environment at the nanoscale," he said.
"This research paves the way towards a new class of quantum sensors used for biological research into the development of new drugs and nanomedicine."
The sensor is capable of detecting biological processes at a molecular level, such as the regulation of chemicals in and out of the cell, which is critical in understanding how drugs work.
The paper has been published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Funded by the ARC Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology, the research was conducted by a cross-disciplinary team from the University of Melbourne's Physics, Chemistry, and Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering departments.
The researchers developed state of the art technology to control and manipulate the atom in the nanodiamond before inserting it into the human cells in the lab.
Biologist Dr Yan Yan of the University's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering who works in the field of nanomedicine, said the sensor provides critical information about the movement of the nanodiamonds inside the living cell.
"This is important for the new field of nanomedicine where drug delivery is dependant on the uptake of similar sized nanoparticles into the cell."
Quantum physicist and PhD student Liam McGuinness from the University's School of Physics said that monitoring the atomic sensor in a living cell was a significant achievement. "Previously, these atomic level quantum measurements could only be achieved under carefully controlled conditions of a physics lab," he said.
It is hoped in the next few years, that following these proof of principle experiments, the researchers will be able to develop the technology and provide a new set of tools for drug discovery and nanomedicine.
####
About University of Melbourne
Established in 1853, the University of Melbourne is a public-spirited institution that makes distinctive contributions to society in research, teaching and engagement.
Melbourne's teaching excellence has been rewarded two years in a row by grants from the Commonwealth Government's Learning and Teaching Performance Fund for Australian universities that demonstrate excellence in undergraduate teaching and learning.
Melbourne was also one of only three Australian universities to win ten citations-the maximum number of awards possible-under the Carrick Citations for Outstanding Contributions to Student Learning. The citations recognise commitment by university staff who have shown outstanding leadership and innovation in teaching, and dedication and enthusiasm for student learning.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Rebecca Scott
University of Melbourne
Mobile: 0417164791
Copyright © University of Melbourne
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








