Home > Press > Clay-armored bubbles may have formed first protocells
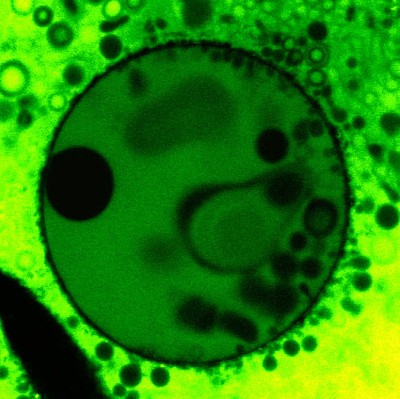 |
| This false-color confocal image shows fatty-acid liposomes compartmentalized in a clay vesicle. The clay vesicles are approximately 100 microns in diameter, and the pores in the clay tend to range in size from about 50 to 100 nanometers (nm), with a very small percentage of vesicles able to exclude molecules as small as 17 nm. Fatty acid molecules, thought to be the components of primitive organic cell membranes, have been shown to travel through the pores into the vesicle and automatically assemble into micron-sized liposomes. Photo courtesy of Anand Bala Subramaniam. |
Abstract:
Discovery of inorganic, semipermeable clay vesicles indicates minerals could have played a key role in the origins of life.
Clay-armored bubbles may have formed first protocells
Cambridge, MA | Posted on February 8th, 2011A team of applied physicists at Harvard's School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Princeton, and Brandeis have demonstrated the formation of semipermeable vesicles from inorganic clay.
The research, published online this week in the journal Soft Matter, shows that clay vesicles provide an ideal container for the compartmentalization of complex organic molecules.
The authors say the discovery opens the possibility that primitive cells might have formed inside inorganic clay microcompartments.
"A lot of work, dating back several decades, explores the role of air bubbles in concentrating molecules and nanoparticles to allow interesting chemistry to occur," says lead author Anand Bala Subramaniam, a doctoral candidate at SEAS.
"We have now provided a complete physical mechanism for the transition from a two-phase clay-air bubble system, which precludes any aqueous-phase chemistry, to a single aqueous-phase clay vesicle system," Subramaniam says, "creating a semipermeable vesicle from materials that are readily available in the environment."
"Clay-armored bubbles" form naturally when platelike particles of montmorillonite collect on the outer surface of air bubbles under water.
When the clay bubbles come into contact with simple organic liquids like ethanol and methanol, which have a lower surface tension than water, the liquid wets the overlapping plates. As the inner surface of the clay shell becomes wet, the disturbed air bubble inside dissolves.
The resulting clay vesicle is a strong, spherical shell that creates a physical boundary between the water inside and the water outside. The translucent, cell-like vesicles are robust enough to protect their contents in a dynamic, aquatic environment such as the ocean.
Microscopic pores in the vesicle walls create a semipermeable membrane that allows chemical building blocks to enter the "cell," while preventing larger structures from leaving.
Scientists have studied montmorillonite, an abundant clay, for hundreds of years, and the mineral is known to serve as a chemical catalyst, encouraging lipids to form membranes and single nucleotides to join into strands of RNA.
Because liposomes and RNA would have been essential precursors to primordial life, Subramaniam and his coauthors suggest that the pores in the clay vesicles could do double duty as both selective entry points and catalytic sites.
"The conclusion here is that small fatty acid molecules go in and self-assemble into larger structures, and then they can't come out," says principal investigator Howard A. Stone, the Dixon Professor in Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at Princeton, and a former Harvard faculty member. "If there is a benefit to being protected in a clay vesicle, this is a natural way to favor and select for molecules that can self-organize."
Future research will explore the physical interactions between the platelike clay particles, and between the liquids and the clay. The researchers are also interested to see whether these clay vesicles can, indeed, be found in the natural environment today.
"Whether clay vesicles played a significant role in the origins of life is of course unknown," says Subramaniam, "but the fact that they are so robust, along with the well-known catalytic properties of clay, suggests that they may have had some part to play."
Subramaniam and Stone's coauthors include Jiandi Wan, of Princeton University, and Arvind Gopinath, of Brandeis University.
The research was funded by the Harvard Materials Research Science and Engineering Center and supported by the Harvard Center for Brain Science Imaging Facility.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caroline Perry
617-496-3815
Copyright © Harvard University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Self Assembly
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








