Home > Press > Tiny Channels Carry Big Information
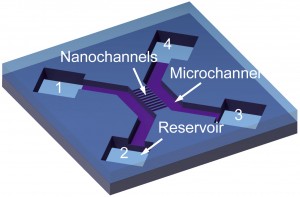 |
| Schematic of a 2-nm nanochannel device, with two microchannels, ten nanochannels and four reservoirs. (Image courtesy of Chuanhua Duan) |
Abstract:
Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have been able to fabricate nanochannels that are only two nanometers (2-nm) in size.
Tiny Channels Carry Big Information
Berkeley, CA | Posted on December 15th, 2010They say it's the little things that count, and that certainly holds true for the channels in transmembrane proteins, which are small enough to allow ions or molecules of a certain size to pass through, while keeping out larger objects. Artificial fluidic nanochannels that mimic the capabilities of transmembrane proteins are highly prized for a number of advanced technologies. However, it has been difficult to make individual artificial channels of this size - until now.
Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have been able to fabricate nanochannels that are only two nanometers (2-nm) in size, using standard semiconductor manufacturing processes. Already they've used these nanochannels to discover that fluid mechanics for passages this small are significantly different not only from bulk-sized channels, but even from channels that are merely 10 nanometers in size.
"We were able to study ion transport in our 2-nm nanochannels by measuring the time and concentration dependence of the ionic conductance," says Arun Majumdar, Director of DOE's Advanced Research Projects Agency - Energy (ARPA-E), who led this research while still a scientist at Berkeley Lab. "We observed a much higher rate of proton and ionic mobility in our confined hydrated channels - up to a fourfold increase over that in larger nanochannels (10-to-100 nm). This enhanced proton transport could explain the high throughput of protons in transmembrane channels."
Majumdar is the co-author with Chuanhua Duan, a member of Majumdar's research group at the University of California (UC) Berkeley, of a paper on this work, which was published in the journal Nature Nanotechnlogy. The paper is titled "Anomalous ion transport in 2-nm hydrophilic nanochannels."
In their paper, Majumdar and Duan describe a technique in which high-precision ion etching is combined with anodic bonding to fabricate channels of a specific size and geometry on a silicon-on-glass die. To prevent the channel from collapsing under the strong electrostatic forces of the anodic bonding process, a thick (500 nm) oxide layer was deposited onto the glass substrate.
"This deposition step and the following bonding step guaranteed successful channel sealing without collapsing," says Duan. "We also had to choose the right temperature, voltage and time period to ensure perfect bonding. I compare the process to cooking a steak, you need to choose the right seasoning as well as the right time and temperature. The deposition of the oxide layer was the right seasoning for us."
The nanometer-sized channels in transmembrane proteins are critical to controlling the flow of ions and molecules across the external and internal walls of a biological cell, which, in turn, are critical to many of the biological processes that sustain the cell. Like their biological counterparts, fluidic nanochannels could play critical roles in the future of fuel cells and batteries.
"Enhanced ion transport improves the power density and practical energy density of fuel cells and batteries," Duan says. "Although the theoretical energy density in fuel cells and batteries is determined by the active electrochemical materials, the practical energy density is always much lower because of internal energy loss and the usage of inactive components. Enhanced ion transport could reduce internal resistance in fuel cells and batteries, which would reduce the internal energy loss and increase the practical energy density."
The findings by Duan and Majumdar indicate that ion transport could be significantly enhanced in 2-nm hydrophilic nanostructures because of their geometrical confinements and high surface-charge densities. As an example, Duan cites the separator, the component placed between the between the cathode and the anode in batteries and fuel cells to prevent physical contact of the electrodes while enabling free ionic transport.
"Current separators are mostly microporous layers consisting of either a polymeric membrane or non-woven fabric mat," Duan says. "An inorganic membrane embedded with an array of 2-nm hydrophilic nanochannels could be used to replace current separators and improve practical power and energy density."
The 2-nm nanochannels also hold promise for biological applications because they have the potential to be used to directly control and manipulate physiological solutions. Current nanofluidic devices utilize channels that are 10-to-100 nm in size to separate and manipulate biomolecules. Because of problems with electrostatic interactions, these larger channels can function with artificial solutions but not with natural physiological solutions.
"For physiological solutions with typical ionic concentrations of approximately 100 millimolars, the Debye screening length is 1 nm," says Duan. "Since electrical double layers from two-channel surfaces overlap in our 2-nm nanochannels, all current biological applications found in larger nanochannels can be transferred to 2-nm nanochannels for real physiological media."
The next step for the researchers will be to study the transport of ions and molecules in hydrophilic nanotubes that are even smaller than 2-nm. Ion transport is expected to be even further enhanced by the smaller geometry and stronger hydration force.
"I am developing an inorganic membrane with embedded sub-2 nm hydrophilic nanotube array that will be used to study ion transport in both aqueous and organic electrolytes,' Duan says. "It will also be developed as a new type of separator for lithium-ion batteries."
This work was supported by DOE's Office of Science, plus the Center for Scalable and Integrated Nanomanufacturing, and the Center of Integrated Nanomechanical Systems at UC Berkeley.
Additional Information
For more information about the research of Arun Majumdar visit http://www.me.berkeley.edu/faculty/majumdar/
For more information about ARPA-E visit the Website at arpa-e.energy.gov/
For more information about the Center for Scalable and Integrated Nanomanufacturing (SINAM) visit www.sinam.org/
For more information about the Center of Integrated Nanomechanical Systems (COINS), visit mint.physics.berkeley.edu/coins/
####
About Berkeley Lab
Berkeley Lab is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory located in Berkeley, California. It conducts unclassified scientific research and is managed by the University of California for the DOE Office of Science.
Visit our Website at www.lbl.gov
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
(510) 486-5375
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Implantable device shrinks pancreatic tumors: Taming pancreatic cancer with intratumoral immunotherapy April 14th, 2023
Implantable device shrinks pancreatic tumors: Taming pancreatic cancer with intratumoral immunotherapy April 14th, 2023
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Oregon State University research pushes closer to new therapy for pancreatic cancer May 6th, 2022
Oregon State University research pushes closer to new therapy for pancreatic cancer May 6th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Fuel Cells
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








