Home > Press > Study uncovers redox response properties of largest-ever polymeric o-phenylenes
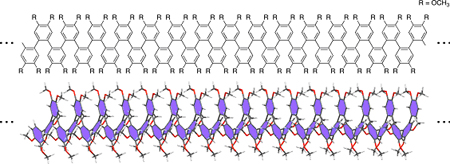 |
| Figure 1: (Top) Molecular formula of a polymeric o-phenylene. (Bottom) Schematic illustration of a helical structure of polymeric o-phenylene. |
Abstract:
New findings by researchers at RIKEN and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) have shed light on the remarkable electrochemical response properties of an elusive class of molecular helix structures, charting a new path in the design of molecular machines and devices.
Study uncovers redox response properties of largest-ever polymeric o-phenylenes
UK | Posted on November 16th, 2010Among the most ubiquitous structural motifs in nature, helices play an essential role in a wide range of biological processes. The capacity of certain helix structures to respond to external stimuli by changing shape, in particular, offers key insights in the design of functional molecular devices. As of yet, however, few such structures have been identified that respond to electrochemical inputs, one of the most important types of stimuli.
Now a class of helical structures has been found to do this, and more. o-Phenylenes are densely-packed chains of phenylene (C6H4) compounds linked together at their ortho positions by heavily-angled connections. Despite potentially rich conformational behavior, o-phenylenes are difficult to study and have been all but forgotten since their discovery more than 50 years ago.
In a paper in Nature Chemistry, the RIKEN/JST research group demonstrates a method for synthesizing polymeric o-phenylenes on scales never before observed, the largest reaching some 48 phenylene units. Problems of electrochemical instability which plagued earlier studies are solved by introducing a nitrogen group to the end of the o-phenylene chain, enabling first-ever exploration of o-phenylene oxidation-reduction response.
Experiments with the new o-phenylenes revealed intriguing results. In solution, the helices depart from their folded form to undergo rapid inversion between clockwise and anti-clockwise orientations, yet when they crystallize, they converge uniformly to only one orientation, in a rare process called chiral symmetry-breaking. Removal of a single electron, meanwhile, converts helices across the entire solution to a more compact form, slowing the inversion rate by a factor of more than 450.
Through its parallel to permanent and long-lasting memory, this unique form of conformational rigidity alterable by electrical inputs offers a completely new design concept for nanotechnology, opening new avenues for the design of molecular wires and other nano-scale devices.
Reference:
Eisuke Ohta, Hiroyasu Sato, Shinji Ando, Atsuko Kosaka, Takanori Fukushima, Daisuke Hashizume, Mikio Yamasaki, Kimiko Hasegawa, Azusa Muraoka, Hiroshi Ushiyama and Takuzo Aida. Redox-responsive molecular helices with highly condensed p -clouds. Nature Chemistry (2010). DOI:10.1038/NCHEM.900
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Takuzo Aida
Functional Soft Matter Research Group
RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
Tel: +81-(0)3-5841-7251
Fax: +81-(0)3-5841-7310
Ms. Tomoko Ikawa (PI officer)
Global Relations Office
RIKEN
Tel: +81-(0)48-462-1225
Fax: +81-(0)48-463-3687
Copyright © ResearchSEA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








