Home > Press > Quantum simulations uncover hydrogen’s phase transitions
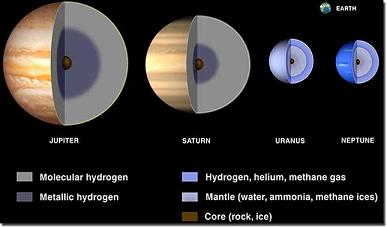 |
| As indicated in the graphic, the gas giant planets of our solar system – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune – are mostly composed of hydrogen. Image courtesy of NASA |
Abstract:
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and is a major component of giant planets such as Jupiter and Saturn. But not much is known about what happens to this abundant element under high-pressure conditions when it transforms from one state to another.
Quantum simulations uncover hydrogen’s phase transitions
Livermore, CA | Posted on July 7th, 2010Using quantum simulations, scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the University of L'Aquia in Italy were able to uncover these phase transitions in the laboratory similar to how they would occur in the centers of giant planets.
They discovered a first order phase transition, a discontinuity, in liquid hydrogen between a molecular state with low conductivity and a highly conductive atomic state. The critical point of the transition occurs at high temperatures, near 3100 degrees Fahrenheit and more than 1 million atmospheres of pressure.
"This research sheds light on the properties of this ubiquitous element and may aid in efforts to understand the formation of planets," said LLNL's Eric Schwegler.
The team used a variety of sophisticated quantum simulation approaches to examine the onset of molecular diassociation in hydrogen under high-pressure conditions. The simulations indicated there is a range of densities where the electrical conductivity of the fluid increases in a discontinuous fashion for temperatures below 3100 degrees Fahrenheit.
There is a liquid-liquid-solid multiphase coexistence point in the hydrogen phase diagram that corresponds to the intersection of the liquid-liquid phase transition, according to Miguel Morales from the University of Illinois and lead author of a paper appearing online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences for the week of June 21-25.
Other collaborators include Prof. David Ceperley from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Prof. Carlo Pierleoni from the University of L'Aquila. The work was funded in part by the National Nuclear Security Administration under the Stewardship Science Academic Alliances program.
####
About Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is a national security laboratory, with a mission to ensure national security and apply science and technology to the important issues of our time. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne M. Stark
(925) 422-9799
Copyright © Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








