Home > Press > New molecular framework could lead to flexible solar cells
 |
| The Dichtel group in the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology has developed a method to organize organic dyes into stacked, porous two-dimensional sheets. These materials may ultimately be incorporated into inexpensive, flexible solar cells. Courtesy Cornell University |
Abstract:
Team discovers simple process for building an organic molecular framework that could pave the way for the development of more economical, flexible and versatile solar cells
By Lauren Gold
New molecular framework could lead to flexible solar cells
Ithaca, NY | Posted on July 2nd, 2010Think of solar cells, and you probably imagine the thick, heavy silicon panels on rooftops in sunny climates.
Those panels are effective, but they can also be expensive and unwieldy. In the search for a better alternative, a team led by William Dichtel, assistant professor of chemistry and chemical biology, has discovered a simple process for building an organic molecular framework that could pave the way for the development of more economical, flexible and versatile solar cells.
The discovery is reported in an article published online on June 20 by the journal Nature Chemistry.
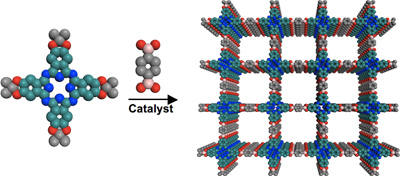
Dichtel's strategy uses organic dye molecules assembled into a structure known as a covalent organic framework (COF). Organic materials have long been recognized as having potential to create thin, flexible and low-cost photovoltaic devices, but it has been proven difficult to organize their component molecules reliably into ordered structures likely to maximize device performance.
COFs, a class of materials first reported in 2005, offer a new way to address this long-range ordering problem; but until now, the known methods for creating them had significant limitations.
"We had to develop a completely new way of making the materials in general," Dichtel said. The strategy uses a simple acid catalyst and relatively stable molecules called protected catechols to assemble key organic molecules into a neatly ordered two-dimensional sheet. These sheets stack on top of one another to form a lattice that provides pathways for charge to move through the material.
The reaction is also reversible, allowing for errors in the process to be undone and corrected.
"The whole system is constantly forming wrong structures alongside the correct one," Dichtel said, "but the correct structure is the most stable, so eventually, the more perfect structures end up dominating." The result is a structure with high surface area that maintains its precise and predictable molecular ordering over large areas.
The researchers used X-ray diffraction to confirm the material's molecular structure and surface area measurements to determine its porosity.
At the core of the framework are molecules called phthalocyanines, a class of common industrial dyes used in products from blue jeans to ink pens.
Phthalocyanines are also closely related in structure to chlorophyll, the compound in plants that absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis. The compounds absorb almost the entire solar spectrum -- a rare property for a single organic material.
"For most organic materials used for electronics, there's a combination of some design to get the materials to perform well enough, and there's a little bit of an element of luck," Dichtel said. "We're trying to remove as much of that element of luck as we can."
The structure by itself is not a solar cell yet, but it is a model that will significantly broaden the scope of materials that can be used in COFs, Dichtel said. "We also hope to take advantage of their structural precision to answer fundamental scientific questions about moving electrons through organic materials."
Once the framework is assembled, the pores between the molecular latticework could potentially be filled with another organic material to form a light, flexible, highly efficient and easy-to-manufacture solar cell.
The next step is to begin testing ways of filling in the gaps with complementary molecules. "This is the very beginning of our work," he said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Cornell Chronicle:
Lauren Gold
(607) 255-9736
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








