Home > Press > Brown University Scientists Discover New Principle in Material Science
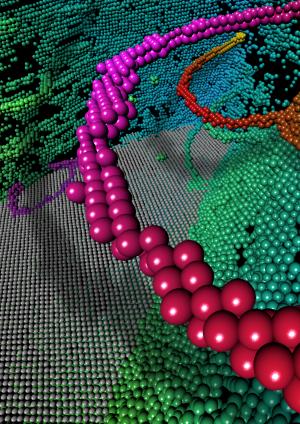 |
| Atomic Strength: A material science team led by Brown University engineers has found that the deformation of nanotwinned metals is characterized by the motion of highly ordered, necklace-like patterns of crystal defects called dislocations. Credit: Huajian Gao and Xiaoyan Li/Brown University |
Abstract:
A material science team led by Brown University engineers has found that the deformation of nanotwinned metals is characterized by the motion of highly ordered, necklace-like patterns of crystal defects called dislocations.
Brown University Scientists Discover New Principle in Material Science
Providence, RI | Posted on April 8th, 2010Materials scientists have known that a metal's strength (or weakness) is governed by dislocation interactions, a messy exchange of intersecting fault lines that move or ripple within metallic crystals. But what happens when metals are engineered at the nanoscale? Is there a way to make metals stronger and more ductile by manipulating their nanostructures?
Brown University scientists may have figured out a way. In a paper published in Nature, Huajian Gao and researchers from the University of Alabama and China report a new mechanism that governs the peak strength of nanostructured metals. By performing 3-D atomic simulations of divided grains of nanostructured metals, Gao and his team observed that dislocations organize themselves in highly ordered, necklace-like patterns throughout the material. The nucleation of this dislocation pattern is what determines the peak strength of materials, the researchers report.
The finding could open the door to producing stronger, more ductile metals, said Gao, professor of engineering at Brown. "This is a new theory governing strength in materials science," he added. "Its significance is that it reveals a new mechanism of material strength that is unique for nanostructured materials."
Divide a grain of metal using a specialized technique, and the pieces may reveal boundaries within the grain that scientists refer to as twin boundaries. These are generally flat, crystal surfaces that mirror the crystal orientations across them. The Chinese authors created nanotwinned boundaries in copper and were analyzing the space between the boundaries when they made an interesting observation: The copper got stronger as the space between the boundaries decreased from 100 nanometers, ultimately reaching a peak of strength at 15 nanometers. However, as the spacing decreased from 15 nanometers, the metal got weaker.
"This is very puzzling," Gao said.
So Gao and Brown graduate student Xiaoyan Li dug a little further. The Brown scientists reproduced their collaborators' experiment in computer simulations involving 140 million atoms. They used a supercomputer at the National Institute for Computational Sciences in Tennessee, which allowed them to analyze the twin boundaries at the atomic scale. To their surprise, they saw an entirely new phenomenon: A highly ordered dislocation pattern controlled by nucleation had taken hold and dictated the copper's strength. The pattern was characterized by groups of atoms near the dislocation core and assembled in highly ordered, necklace-like patterns.
"They're not getting in each other's way. They're very organized," Gao said.
From the experiments and the computer modeling, the researchers theorize that at the nanoscale, dislocation nucleation can become the governing principle to determining a metal's strength or weakness. The authors presented a new equation in the Nature paper to describe the principle.
"Our work provides a concrete example of a source-controlled deformation mechanism in nanostructured materials for the first time and, as such, can be expected to have a profound impact on the field of materials science," Gao said.
The other researchers who contributed to the paper are Yujie Wei from the University of Alabama and Ke Lu and Lei Lu from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The U.S. National Science Foundation, the National Science Foundation in China and the Ministry of Science and Technology in China funded the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Richard Lewis
(401) 863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








