Home > Press > A step toward lighter batteries
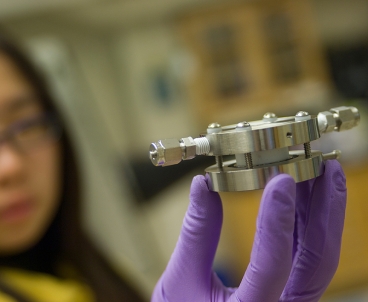 |
| Doctoral student Yi-Chun Lu holds an experimental lithium-air battery that was used for testing at MIT. Photo: Patrick Gillooly |
Abstract:
Research shows metal catalysts play important role in improving the efficiency of lithium-oxygen batteries.
By David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
A step toward lighter batteries
Cambridge, MA | Posted on April 2nd, 2010Lightweight batteries that can deliver lots of energy are crucial for a variety of applications — for example, improving the range of electric cars. For that reason, even modest increases in a battery's energy-density rating — a measure of the amount of energy that can be delivered for a given weight — are important advances. Now a team of researchers at MIT has made significant progress on a technology that could lead to batteries with up to three times the energy density of any battery that currently exists.
Yang Shao-Horn, an MIT associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and engineering, says that many groups have been pursuing work on lithium-air batteries, a technology that has great potential for achieving great gains in energy density. But there has been a lack of understanding of what kinds of electrode materials could promote the electrochemical reactions that take place in these batteries.
Lithium-oxygen (also known as lithium-air) batteries are similar in principle to the lithium-ion batteries that now dominate the field of portable electronics and are a leading contender for electric vehicles. But because lithium-air batteries use lightweight porous carbon electrodes and oxygen drawn from a flow of air to take the place of heavy solid compounds used in lithium-ion batteries, the batteries themselves can be much lighter. That's why leading companies, including IBM and General Motors, have committed to major research initiatives on lithium-air technology.
In a paper published this week in the journal Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, Shao-Horn, along with some of her students and visiting professor Hubert Gasteiger, reported on a study showing that electrodes with gold or platinum as a catalyst show a much higher level of activity and thus a higher efficiency than simple carbon electrodes in these batteries. In addition, this new work sets the stage for further research that could lead to even better electrode materials, perhaps alloys of gold and platinum or other metals, or metallic oxides, and to less expensive alternatives.
Doctoral student Yi-Chun Lu, lead author of the paper, explains that this team has developed a method for analyzing the activity of different catalysts in the batteries, and now they can build on this research to study a variety of possible materials. "We'll look at different materials, and look at the trends," she says. "Such research could allow us to identify the physical parameters that govern the catalyst activity. Ultimately, we will be able to predict the catalyst behaviors. "
One issue to be dealt with in developing a battery system that could be widely commercialized is safety. Lithium in metallic form, which is used in lithium-air batteries, is highly reactive in the presence of even minuscule amounts of water. This is not an issue in current lithium-ion batteries because carbon-based materials are used for the negative electrode. Shao-Horn says the same battery principle can be applied without the need to use metallic lithium; graphite or some other more stable negative electrode materials could be used instead, she says, leading to a safer system.
A number of issues must be addressed before lithium-air batteries can become a practical commercial product, she says. The biggest issue is developing a system that keeps its power through a sufficient number of charging and discharging cycles for it to be useful in vehicles or electronic devices.
Researchers also need to look into details of the chemistry of the charging and discharging processes, to see what compounds are produced and where, and how they react with other compounds in the system. "We're at the very beginning" of understanding exactly how these reactions occur, Shao-Horn says.
Gholam-Abbas Nazri, a researcher at the GM Research & Development Center in Michigan, calls this research "interesting and important," and says this addresses a significant bottleneck in the development of this technology: the need find an efficient catalyst. This work is "in the right direction for further understanding of the role of catalysts," and it "may significantly contribute to the further understanding and future development of lithium-air systems," he says.
While some companies working on lithium-air batteries have said they see it as a 10-year development program, Shao-Horn says it is too early to predict how long it may take to reach commercialization. "It's a very promising area, but there are many science and engineering challenges to be overcome," she says. "If it truly demonstrates two to three times the energy density" of today's lithium-ion batteries, she says, the likely first applications will be in portable electronics such as computers and cell phones, which are high-value items, and only later would be applied to vehicles once the costs are reduced.
####
About MIT
The mission of MIT is to advance knowledge and educate students in science, technology and other areas of scholarship that will best serve the nation and the world in the 21st century — whether the focus is cancer, energy, economics or literature.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








