Home > Press > Blueprint for “artificial leaf” mimics Mother Nature
 |
| Part of the recipe for an artificial leaf, which draws on Mother Nature’s secrets, and could use sunlight and water to produce fuel. |
Abstract:
Scientists today (March 25) presented a design strategy to produce the long-sought artificial leaf, which could harness Mother Nature's ability to produce energy from sunlight and water in the process called photosynthesis. The new recipe, based on the chemistry and biology of natural leaves, could lead to working prototypes of an artificial leaf that capture solar energy and use it efficiently to change water into hydrogen fuel, they stated.
Blueprint for “artificial leaf” mimics Mother Nature
San Francisco, CA | Posted on March 29th, 2010Their report was scheduled for the 239th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS), being held here this week. It was among more than 12,000 scientific reports scheduled for presentation at the meeting, one of the largest scientific gatherings of 2010.
"This concept may provide a new vista for the design of artificial photosynthetic systems based on biological paradigms and build a working prototype to exploit sustainable energy resources," Tongxiang Fan, Ph.D. and colleagues Di Zhang, Ph.D. and Han Zhou, Ph.D., reported, They are with the State Key Lab of Matrix Composites at Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China.
Fan pointed out that using sunlight to split water into its components, hydrogen and oxygen, is one of the most promising and sustainable tactics to escape current dependence on coal, oil, and other traditional fuels. When burned, those fuels release carbon dioxide, the main greenhouse gas. Combustion of hydrogen, in contrast, forms just water vapor. That appeal is central to the much-discussed "Hydrogen Economy," and some auto companies, such as Toyota, have developed hydrogen-fueled cars. Lacking, however, is a cost-effective sustainable way to produce hydrogen.
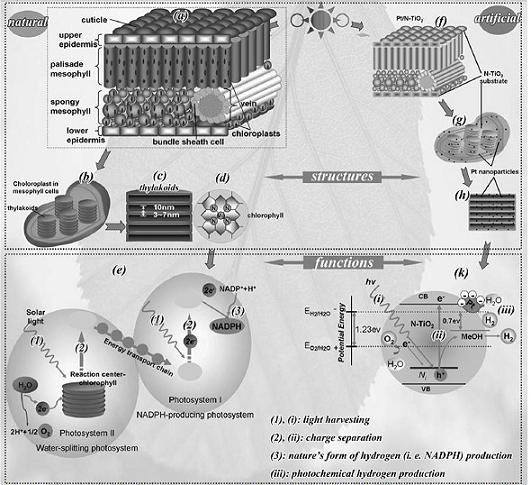
With that in mind, Fan and co-workers decided to take a closer look at the leaf, nature's photosynthetic system, with plans to use its structure as a blueprint for their next generation of artificial systems. Not too surprisingly, the structure of green leaves provides them an extremely high light-harvesting efficiency. Within their architecture are structures responsible focusing and guiding of solar energy into the light-harvesting sections of the leaf, and other functions.
The scientists decided to mimic that natural design in the development of a blueprint for artificial leaf-like structures. It led them to report their recipe for the "Artificial Inorganic Leaf" (AIL), based on the natural leaf and titanium dioxide (TiO2) — a chemical already recognized as a photocatalyst for hydrogen production.
The scientists first infiltrated the leaves of Anemone vitifolia - a plant native to China - with titanium dioxide in a two-step process. Using advanced spectroscopic techniques, the scientists were then able to confirm that the structural features in the leaf favorable for light harvesting were replicated in the new TiO2 structure. Excitingly, the AIL are eight times more active for hydrogen production than TiO2 that has not been "biotemplated" in that fashion. AILs also are more than three times as active as commercial photo-catalysts. Next, the scientists embedded nanoparticles of platinum into the leaf surface. Platinum, along with the nitrogen found naturally in the leaf, helps increase the activity of the artificial leaves by an additional factor of ten.
In his ACS presentation, Fan reported on various aspects of Artificial Inorganic Leaf production, their spectroscopic work to better understand the macro- and microstructure of the photocatalysts, and their comparison to previously reported systems. The activity of these new "leaves", are significantly higher than those prepared with classic routes. Fan attributes these results to the hierarchical structures derived from natural leaves:
"Our results may represent an important first step towards the design of novel artificial solar energy transduction systems based on natural paradigms, particularly based on exploring and mimicking the structural design. Nature still has much to teach us, and human ingenuity can modify the principles of natural systems for enhanced utility."
####
About American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world’s largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
415-978-3504 (Meeting, March 21-25)
Michael Woods
415-978-3504 (Meeting, March 21-25)
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Events/Classes
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








