Home > Press > Lower-Cost Solar Cells to Be Printed Like Newspaper, Painted on Rooftops
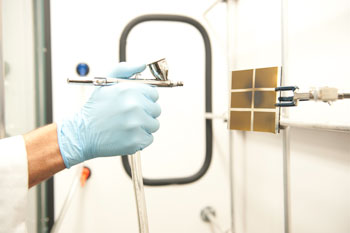 |
| Researchers apply the nanoparticle "inks" as a spray on the solar cells. |
Abstract:
Solar cells could soon be produced more cheaply using nanoparticle "inks" that allow them to be printed like newspaper or painted onto the sides of buildings or rooftops to absorb electricity-producing sunlight.
Lower-Cost Solar Cells to Be Printed Like Newspaper, Painted on Rooftops
Austin, TX | Posted on August 24th, 2009Brian Korgel, a University of Texas at Austin chemical engineer, is hoping to cut costs to one-tenth of their current price by replacing the standard manufacturing process for solar cells—gas-phase deposition in a vacuum chamber, which requires high temperatures and is relatively expensive.
"That's essentially what's needed to make solar-cell technology and photovoltaics widely adopted," Korgel said. "The sun provides a nearly unlimited energy resource, but existing solar energy harvesting technologies are prohibitively expensive and cannot compete with fossil fuels."
For the past two years, Korgel and his team have been working on this low-cost, nanomaterials solution to photovoltaics—or solar cell—manufacturing. Korgel is collaborating with professors Al Bard and Paul Barbara, both of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, and Professor Ananth Dodabalapur of the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. They recently showed proof-of-concept in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The inks could be printed on a roll-to-roll printing process on a plastic substrate or stainless steel. And the prospect of being able to paint the "inks" onto a rooftop or building is not far-fetched.
"You'd have to paint the light-absorbing material and a few other layers as well," Korgel said. "This is one step in the direction towards paintable solar cells."
Korgel uses the light-absorbing nanomaterials, which are 10,000 times thinner than a strand of hair, because their microscopic size allows for new physical properties that can help enable higher-efficiency devices.
In 2002, he co-founded a company called Innovalight, based in California, which is producing inks using silicon as the basis. This time, Korgel and his team are using copper indium gallium selenide or CIGS, which is both cheaper and benign in terms of environmental impact.
"CIGS has some potential advantages over silicon," Korgel said. "It's a direct band gap semiconductor, which means that you need much less material to make a solar cell, and that's one of the biggest potential advantages."
His team has developed solar-cell prototypes with efficiencies at one percent; however, they need to be about 10 percent.
"If we get to 10 percent, then there's real potential for commercialization," Korgel said. "If it works, I think you could see it being used in three to five years."
He also said that the inks, which are semi-transparent, could help realize the prospect of having windows that double as solar cells. Korgel said his work has attracted the interest of industrial partners.
Funding for the research comes from the National Science Foundation, the Welch Foundation and the Air Force Research Laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daniel Vargas
Cockrell School of Engineering
512-471-7541
Brian Korgel
Department of Chemical Engineering
Cockrell School of Engineering
512-471-5633
Copyright © University of Texas at Austin
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








