Home > Press > Fluorescence or flexibility
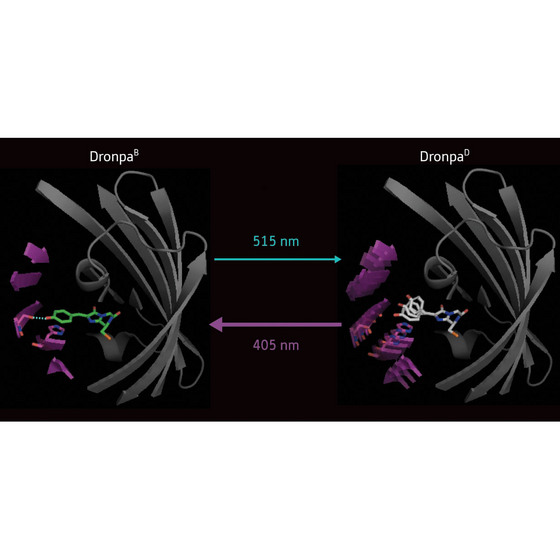 |
| Figure 1: Comparison of the bright (DronpaB) and dark (DronpaD) states of the Dronpa protein. In the bright state, the chromophore (green) is tethered to the molecule by a hydrogen bond (dotted blue line), while in the dark state the hydrogen bond is gone and the chromophore can vibrate.
Copyright © 2008 Atsushi Miyawaki |
Abstract:
Researchers shed light on the molecular mechanism responsible for fluorescent and dark states of a genetically engineered protein
Fluorescence or flexibility
Japan | Posted on October 25th, 2008Some organic substances have a property called photochromism, meaning that their absorption spectrum, or color, changes when they are exposed to certain types of light. In particular, a new artificial protein called Dronpa shows great promise for applications because it can be switched back and forth between a ‘bright' state and a ‘dark' state. Now Atsushi Miyawaki, Hideaki Mizuno at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Wako and co-workers1 have explained for the first time exactly what causes Dronpa to move between these two states.
Dronpa was developed by Miyawaki and colleagues by genetic engineering on a wild coral protein. Usually Dronpa absorbs light of around 503 nanometers wavelength and emits green fluorescence—the so-called bright state. However if it is exposed to strong radiation at 488 nanometers it converts into the dark state, which emits no fluorescence. The protein will switch back to the bright state if it is re-irradiated at an even shorter wavelength.
"Such reliable photochromism for Dronpa prompted us to develop it for information storage with the ability to record, erase, or read information," says Miyawaki. However to date no-one has proven exactly what causes the photochromism.
To unlock this mystery the researchers used nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to study the Dronpa molecule, which takes a cylindrical shape called a β-barrel, like other fluorescent proteins. They discovered that the bright and dark states arise from interactions between the β-barrel and the chromophore—the part of the molecule responsible for light absorption.
In the bright state, the chromophore is tightly tethered to the β-barrel by a hydrogen bond (Fig. 1). This holds the chromophore in a rigid, flat configuration, so that when it is excited by light it releases its excess energy by fluorescing.
When the dark state is induced, the hydrogen bond is lost and the chromophore becomes much more flexible. Therefore it releases the excess energy by vibrating instead of fluorescing.
In other compounds that have been studied, photochromism results from physical rearrangements of atoms in the molecules. This is the first time that photochromism has been linked to structural flexibility.
"We present a new molecular mechanism for photochromism of a fluorescent protein," says Miyawaki. "The mechanism requires a special microenvironment involving a β-barrel, a structure not present in organic photochromic compounds."
Miyawaki hopes that Dronpa could eventually be used in very high-resolution optical microscopy. "The next stage will be to develop many mutants of Dronpa with different photochromic properties," he says.
Reference
1. Mizuno, H., Mal, K.T., Wälchli, M., Kikuchi, A., Fukano, T., Ando, R., Jeyakanthan, J., Taka, J., Shiro, Y., Ikura, M. & Miyawaki, A. Light-dependent regulation of structural flexibility in a photochromic fluorescent protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 105, 9927-9932 (2008).
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the RIKEN Laboratory for Cell Function Dynamics
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Riken
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








