Home > Press > When a light goes on during thought processes: Fluorescent proteins in the brain light up during individual action potentials making it possible to tr
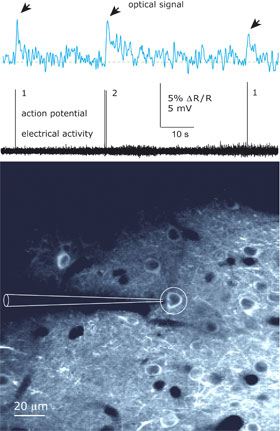 |
| Individual and double action potentials can be recorded optically using a genetic calcium indicator that colours the cells in the brain of a living mouse.
Image: Max Planck Institute for Medical Research |
Abstract:
Thought processes made visible: An international team of scientists headed by Mazahir Hasan of the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg has succeeded in optically detecting individual action potentials in the brains of living animals. The scientists introduced fluorescent indicator proteins into the brain cells of mice via viral gene vectors: the illumination of the fluorescent proteins indicates both when and which neurons are communicating with each other. This new method enables the observation of brain activity over a period of many months and provides new ways of identifying, for example, the early onset of dysfunction in neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. The fluorescent proteins could also provide scientists with information about the ways in which normal aging processes affect nerve cell communication. (Nature Methods, September 2008)
When a light goes on during thought processes: Fluorescent proteins in the brain light up during individual action potentials making it possible to tr
Heidelberg, Germany | Posted on October 6th, 2008A nerve cell is a major hub for the exchange of valuable information. The nose, eyes, ears, and other sense organs perceive our environment through various antennae known as receptors. The numerous stimuli are then passed on to the neurons. All of this information is collected, processed, and finally transferred to specific brain centers at these hubs - the human brain consists of almost 100 billion nerve cells. The nerve cell uses a special means of transport for this purpose: the action potential which codes the information, thus enabling communication between the nerve cells.
Calcium as the starting gun
An action potential of this kind is an electrical excitation and arises when our nerve cells receive the information via a stimulus: the voltage across the cell membrane of the neuron changes and various ion channels open and close in a very specialized manner. Shortly before the nerve cell forwards the information via the stimulus, calcium ions pour into the nerve cell, acting as the starting gun for the flow of data from one neuron to the next.
In the past, action potential was measured and rendered visible using microelectrodes. However, this method only enabled the monitoring of a limited number of cells engaged in the process of communication. Moreover, scientists were unable to record neuronal communication in a clearly identifiable way over a longer period or in freely moving animals using this method.
Yellow and blue fluorescent proteins
This situation could be set to change. As part of an intensive international cooperation project, Mazahir Hasan has made nerve cells, which release a single action potential, optically visible in mice. This means that the communication of entire groups of neurons can be observed over an extended period of time. Mazahir Hasan also attracted attention in 2004 when he demonstrated for the first time that fluorescent proteins are suitable for making activity in the brains of mice visible (Hasan et al., 2004 PLoS Biology 2:e163).
For this new recent development, Hasan used a sensor protein called D3cpv, which was generated by Amy Palmer at the Roger Tsien Laboratory of the University of California in San Diego, as a complex of numerous interconnected protein subunits. Two of these subunits react to the binding of calcium ions to the complex: the yellow-fluorescent protein (YFP) lights up and the illuminating power of cyan-fluorescent protein (CFP) declines - a coincidence that would later prove crucial to the success of the study.
The Max Planck scientists introduced the corresponding genetic material - that is the construction manual for this protein complex - into the genetic material of viruses. Hasan and his team then used these viruses as a genetic "ferry" for introducing the genetic material into the brains of mice. The protein complex was actually produced in the nerve cells of the "infected" mice and functions there as an calcium indicator: if the calcium level within a cell increases - which is the case with every action potential - the D3cpv changes form when it binds to calcium. As a result, the two fluorescent proteins, CFP and YFP, move closer to each other and the transmission of energy between the CFP and YFP changes.
"To observe this change, we use a two-photon microscope developed by Winfried Denk", explains Hasan. Each individual action potential that arises due to a stimulus makes itself directly perceivable in the brain through yellow illumination and the simultaneous reduction in the emission of blue light. The two-photon microscope pinpoints the coincidence between the two fluorescent signals very accurately and clearly reveals which nerve cells are communicating and exchanging information with each other and when.
Damian Wallace and Jason Kerr from the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics in Tübingen were able to confirm this finding: targeted electrical recordings of neuronal activity after the triggering of stimulus showed that the colour change actually coincides with the firing of the action potentials. Hasan's method sheds light on which nerve cells will talk to each other and in which time period. However, it is only applicable if the neurons fire action potentials with a frequency of less than one hertz.
Insight into complex thought processes
The researchers were thus able to demonstrate for the first time that genetic calcium indicators provide optical proof of the perceptions of the sensory system in higher organisms. "With this method we can understand, in greater detail, how the human brain regulates complex thought processes and, for example, how it transforms the numerous sensory impressions into long-term memories", says Hasan. Developments resulting from the aging of the nerve cells can also be understood better as a result - "as we now have a way of observing the neurons over longer periods of time," concludes Hasan. Moreover, the sensor proteins could prove very useful in helping researchers to reach a better understanding at the cellular level of neurological diseases including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's chorea.
Original work:
Damian J Wallace, Stephan Meyer zum Alten Borgloh, Simone Astori, Ying Yang, Melanie Bausen, Sebastian Kügler, Amy E Palmer, Roger Y Tsien, Rolf Sprengel, Jason N D Kerr, Winfried Denk & Mazahir T Hasan
Single-spike detection in vitro and in vivo with a genetic Ca2+ sensor
Nature Methods, Vol.5 No. 9, September 2008, 797
Mazahir T Hasan, Rainer W Friedrich, Thomas Euler, Matthew E Larkum, Günter Giese, Matthias Both, Jens Duebel, Jack Waters, Hermann Bujard, Oliver Griesbeck, Roger Y Tsien, Takeharu Nagai, Atsushi Miyawaki, Winfried Denk
Functional fluorescent Ca2+ indicator proteins in transgenic mice under TET control
PLOS Biology, Vol.2 No.6, June 2004, e163
####
About Max Planck Society
The research institutes of the Max Planck Society perform basic research in the interest of the general public in the natural sciences, life sciences, social sciences, and the humanities. In particular, the Max Planck Society takes up new and innovative research areas that German universities are not in a position to accommodate or deal with adequately. These interdisciplinary research areas often do not fit into the university organization, or they require more funds for personnel and equipment than those available at universities. The variety of topics in the natural sciences and the humanities at Max Planck Institutes complement the work done at universities and other research facilities in important research fields. In certain areas, the institutes occupy key positions, while other institutes complement ongoing research. Moreover, some institutes perform service functions for research performed at universities by providing equipment and facilities to a wide range of scientists, such as telescopes, large-scale equipment, specialized libraries, and documentary resources.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Max Planck Society
for the Advancement of Science
Press and Public Relations Department
Hofgartenstrasse 8
D-80539 Munich
Germany
PO Box 10 10 62
D-80084 Munich
Phone: +49-89-2108-1276
Fax: +49-89-2108-1207
Mazahir T. Hasan, PhD
Max-Planck-Institute for Medical Research, Heidelberg
Tel.: +49 6221-486314
Fax: +49 6221-486325
Copyright © Max Planck Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








