Home > Press > Switchable bio-adhesion
 |
Abstract:
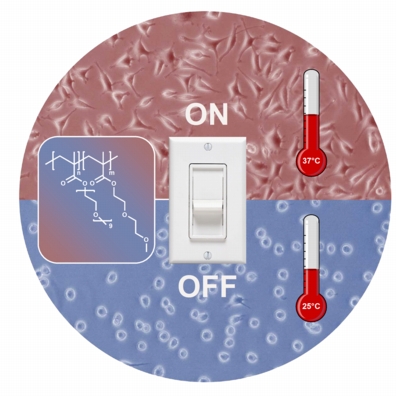
Researchers have developed a new type of property-changing polymer: It is water-repellent at 37°C, which makes it an ideal culture substrate for biological cells. At room temperature it attracts water, allowing the cells to be detached easily from the substrate.
Switchable bio-adhesion
Germany | Posted on September 1st, 2008
What effects do new drugs have on the human body - particularly at cellular level? Can doctors administer them without risk, or do they have toxic side effects? Pharmaceutical companies carry out a variety of toxicity tests on new drugs in order to answer such questions. Cell cultures form the basis for these tests: The researchers place isolated cells in small plastic dishes, add a nutrient solution and place the dishes in an incubator heated to 37 degrees Celsius. To provide an ideal breeding ground for the cells, the dishes are made of insulating polystyrene. Once the cells have multiplied to the required number, the drug is added. However, to examine the cells' reaction to the drug, the researchers then have to remove the cultured cells from the dish. The problem is that the cells often adhere so firmly to the surface of the dish that an enzyme has to be introduced to detach them. "The cells employed in toxicity tests are particularly sensitive, and can be damaged by the added enzyme. This makes it difficult to interpret the test results. It cannot be established without doubt whether the cells' reaction to the drug has been influenced by damage caused by the method used to extract them from the dish" says Dr. Claus Duschl, department head at the Fraunhofer Institute for Biomedical Engineering IBMT in Potsdam-Golm.
A possible solution is the stimuli-responsive polymer developed by a team led by Dr. Jean-François Lutz of the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research IAP, assisted by colleagues at the IBMT and the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces. "At 37 degrees Celsius, the usual incubation temperature for cell cultures, this material is water-repellent (hydrophobic) - the cells feel at ease in this environment and respond by multiplying rapidly. If the substrate is cooled to 25 degrees, equivalent to room temperature, the material becomes hydrophilic (attracts water): The cells try to avoid contact with the substrate by reducing their surface area, curling up into almost spherical shapes. This enables them to be rinsed off easily, so there is no longer any need to add an enzyme," explains Lutz.
This is not the first thermoresponsive polymer. The big difference is that it is based on polyethylene glycol (PEG), which unlike other materials of this type is biocompatible. It is thus an ideal substrate for cell cultures. The new material has the added advantage of being water-soluble and non-toxic. Lutz estimates that it will be possible to mass-produce Petri dishes coated with the new property-changing polymer in about two or three years' time.
####
About Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
The Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft undertakes applied research of direct utility to private and public enterprise and of wide benefit to society.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jean-Francois Lutz
Phone: +49 331 568-1127
Send an e-mail
Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research
IAP
Geiselbergstraße 69
14476 Potsdam-Golm
Copyright © Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








