Home > Press > Max Planck scientists shed light on transport mechanism in cells
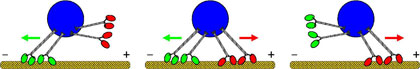 |
| The competition between molecular motors: A blue cargo is transported by two teams of molecular motors moving along the yellow microtubule. The red team of motors is pulling to the right towards the positive end (+), while the green team is pulling to the left towards the minus end (−). When both teams pull (in the center), they cancel each other out so the cargo hardly moves forwards. As soon as one team gains the upper hand, it moves quickly as the opposing motors are removed from the microtubule.
Image: Melanie Müller / MPI of Colloids and Interfaces |
Abstract:
Logistics is a key part of life. Nutrition, tools and information constantly have to be transported from one place to another in cells. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces have now discovered how molecular motors transport cargos in cells. Two competing teams of motors pull in opposite directions, like in a tug-of-war contest. The winning team determines the direction of transport after the competition. (PNAS Early Edition, March 17th 2008)
Max Planck scientists shed light on transport mechanism in cells
Munich, Germany | Posted on March 19th, 2008 Transport processes in the cells of our body resemble the transport of goods on the roads. Molecular motors, which are special protein molecules, act as trucks. They carry the cellular cargo on piggy-back and transport it along microtubules, which are the roads of the cell. However, the molecular transporters are a billion times smaller than trucks and can only move as far as the beginning or end of the microtubule, depending on their type. They have to fight their way through a crowd that is more like a busy pedestrian area than a motorway, and also have to compete with motors that want to move in the opposite direction, as scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam have now discovered in a computer simulation.
Several motors are always involved in the tug-of-war over a cargo - for example, some of the kinesin type and some of the dynein type. The kinesin motors move to the end of the microtubule that biologists call the positive end, while the dynein motors move to the minus end. The findings of the Potsdam-based scientists show that the stronger motor team determines the direction in which the cargo is moved. It involves a tug-of-war where opposing motors break off from the microtubule. It was previously assumed that there was a system of coordination that allowed for only one team of motors; it was believed this alternated between one team and the other.
"The tug-of-war is the simplest imaginable mechanism," says Melanie Müller, one of the scientists involved in the project. "But it is possible, if you consider the properties of the individual motors measured experimentally. They produce a strong non-linear reaction when they are pulled." A motor from the losing team is subject to a strong force and is quickly removed from the microtubule. The remaining motors must then take the force of the winning team alone and are also removed even more quickly. In a domino effect, the losing motors concede and are removed from the microtubule until no others remain. The winning team is then able to transport the cargo quickly, unopposed. "However, the cell does not leave it to chance to ensure that the cargo arrives at its destination. Regulatory proteins probably intervene," says Melanie Müller.
Researchers into the transport of fat particles in Drosophila embryos examined whether her model applied in reality. It is actually explained by experimental observations that took place previously on the transport mechanism. A cargo in a microtubule does not move directly from one end to the other. It is constantly pulled back in the opposite direction. The losing motors can, however, occasionally remove the winning ones from the microtubule as heat sometimes blows the winning motors away. The cargo particles therefore move in both directions.
"This bi-directional transport process is very flexible," explains Melanie Müller. It can change direction if the cargo passes its destination or change the speed of the transport. The tug-of-war mechanism, where the winning team pulls the opposing motor team as well as the cargo through the cell, also solves another logistical problem in the cell. It always carries the motors to the end of the microtubule from which they are able to move, preventing an accumulation of motors of one kind at their respective destination.
"Despite the simple mechanism, a cargo particle transported by two motor teams reveals very complex motility behavior," said Melanie Müller. There are seven different types of motility behavior. These are various combinations of movements to the positive and minus end as well as pauses to which the cargo particles can be subjected. The probability of movement in a certain direction or stopping, and the time lapses between the changes of direction, depend heavily on the properties and the number of the motors involved. The cell uses these to direct the cargo transport. If a team of motors is pulled harder or faster, the cargo moves in the minus instead of the positive direction or stops.
"The simple and efficient tug-of-war mechanism could be used for the transport in micro-laboratories on chips," relates Melanie Müller. In the same way as with the biological model, teams of motors can transport certain molecules to specific reaction locations on the chip and then also bring back the reaction product. "Our quantitative tug-of-war theory allows motor properties to be optimized for this purpose," according to Müller.
[MM / PH]
Original work:
Melanie J.I. Müller, Stefan Klumpp, and Reinhard Lipowsky
Tug-of-war as a cooperative mechanism for bidirectional cargo transport by molecular motors
PNAS Early Edition, March 17th 2008
####
About Max Planck Society
The research institutes of the Max Planck Society perform basic research in the interest of the general public in the natural sciences, life sciences, social sciences, and the humanities. In particular, the Max Planck Society takes up new and innovative research areas that German universities are not in a position to accommodate or deal with adequately. These interdisciplinary research areas often do not fit into the university organization, or they require more funds for personnel and equipment than those available at universities. The variety of topics in the natural sciences and the humanities at Max Planck Institutes complement the work done at universities and other research facilities in important research fields. In certain areas, the institutes occupy key positions, while other institutes complement ongoing research. Moreover, some institutes perform service functions for research performed at universities by providing equipment and facilities to a wide range of scientists, such as telescopes, large-scale equipment, specialized libraries, and documentary resources.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Max Planck Society
for the Advancement of Science
Press and Public Relations Department
Hofgartenstrasse 8
D-80539 Munich
Germany
PO Box 10 10 62
D-80084 Munich
Phone: +49-89-2108-1276
Fax: +49-89-2108-1207
E-mail:
Internet: www.mpg.de/english/
Responsibility for content:
Dr. Bernd Wirsing (-1276)
Executive Editor:
Barbara Abrell (-1416)
Melanie J.I. Müller
Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam
Tel.: +49 331 567-9623
E-mail:
Copyright © Max Planck Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








