Home > Press > All done with mirrors: NIST microscope tracks nanoparticles in 3-D
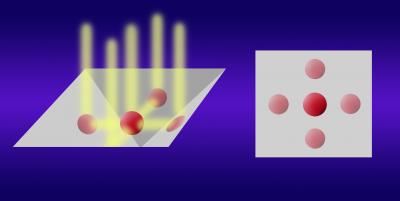 |
| Heart of the orthogonal tracking microscope system developed at NIST is this nanoparticle solution sample well etched in silicon. Careful orientation of the silicon crystal makes it possible to chemically etch angled sides in the well so smooth they act as mirrors. In this configuration, four side views of a nanoparticle floating in solution (left) are reflected up. A microscope above the well sees the real particle (center, right) and four reflections that show the particle's vertical position.
Credit: NIST |
Abstract:
A clever new microscope design allows nanotechnology researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to track the motions of nanoparticles in solution as they dart around in three dimensions. The researchers hope the technology, which NIST plans to patent, will lead to a better understanding of the dynamics of nanoparticles in fluids and, ultimately, process control techniques to optimize the assembly of nanotech devices.
All done with mirrors: NIST microscope tracks nanoparticles in 3-D
GAITHERSBURG, MD | Posted on March 11th, 2008While some nanoscale fabrication techniques borrow from the lithography and solid state methods of the microelectronics industry, an equally promising approach relies on "directed self-assembly." This capitalizes on physical properties and chemical affinities of nanoparticles in solutions to induce them to gather and arrange themselves in desired structures at desired locations. Potential products include extraordinarily sensitive chemical and biological sensor arrays, and new medical and diagnostic materials based on "quantum dots" and other nanoscale materials. But when your product is too small to be seen, monitoring the assembly process is difficult.
Microscopes can help, but a microscope sees a three-dimensional fluid volume as a 2-D plane. There's no real sense of the "up and down" movement of particles in its field of view except that they get more or less fuzzy as they move across the plane where the instrument is in focus. To date, attempts to provide a 3-D view of the movements of nanoparticles in solution largely have relied on that fuzziness. Optics theory and mathematics can estimate how far a particle is above or below the focal plane based on diffraction patterns in the fuzziness. The math, however, is extremely difficult and time consuming and the algorithms are imprecise in practice.
One alternative, NIST researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Physical Society,* is to use geometry instead of algebra. Specifically, angled side walls of the microscopic sample well act as mirrors to reflect side views of the volume up to the microscope at the same time as the top view. (The typical sample well is 20 microns square and 15 microns deep.) The microscope sees each particle twice, one image in the horizontal plane and one in the vertical. Because the two planes have one dimension in common, it's a simple calculation to correlate the two and figure out each particle's 3-D path. "Basically, we reduce the problem of tracking in 3-D to the problem of tracking in 2-D twice," explains lead author Matthew McMahon.
The 2-D problem is simpler to solve—several software techniques can calculate and track 2-D position to better than 10 nanometers. Measuring the nanoparticle motion at that fine scale—speeds, diffusion and the like—will allow researchers to calculate the forces acting on the particles and better understand the basic rules of interaction between the various components. That in turn will allow better design and control of nanoparticle assembly processes.
* M. McMahon, A. Berglund, P. Carmichael, J. McClelland and J.A. Liddle. Orthogonal tracking microscopy for nanofabrication research. Paper presented on Monday, March 10, 2008, 1:03 p.m., at the 2008 March Meeting of the American Physical Society, New Orleans, La., March 10-14, 2008.
####
About NIST
From automated teller machines and atomic clocks to mammograms and semiconductors, innumerable products and services rely in some way on technology, measurement, and standards provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Founded in 1901, NIST is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce. NIST's mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Baum
301-975-2763
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








