Home > Press > Scientists Discover Fluorescence in Key Marine Creature
 |
| Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego
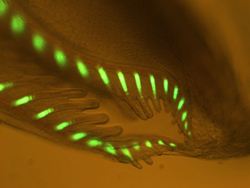
Fluorescence shown along the body structure of amphioxus. |
Abstract:
Researchers say green fluorescent proteins, which could play role as ‘sunscreen' or stress reducer, may be widespread in animal kingdom.
Scientists Discover Fluorescence in Key Marine Creature
San Diego, CA | Posted on October 30th, 2007Fluorescent proteins found in nature have been employed in a variety of scientific research purposes, from markers for tracing molecules in biomedicine to probes for testing environmental quality. Until now, such proteins have been identified mostly in jellyfish and corals, leading to the belief that the capacity for fluorescence in animals is exclusive to such primitive creatures.
Scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego have discovered fluorescent-light emitting features in an evolutionarily important marine organism and say such a capacity may be much more prevalent across the animal kingdom than previously believed.
In the cover story of the October issue of Biological Bulletin, Dimitri Deheyn and his colleagues in La Jolla, Calif. and Japan describe finding green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) in amphioxus, a fish-like animal closely studied by scientists due to its evolutionarily important position at the base of a large phylum of animals called chordates. The researchers say amphioxus' GFPs are very similar to those of corals, an interesting fact since the two animal groups are separated by hundreds of millions of years of evolution.
The finding emphasizes the idea that evolutionary preservation of fluorescence must play an important ecological function, Deheyn said. Many animals haven't been tested for fluorescence and its prevalence in the animal kingdom remains unknown.
Deheyn made the discovery while analyzing a dozen specimens of the small, slender marine animals collected in Tampa, Fla., by Nick Holland, a professor of marine biology at Scripps and a paper coauthor.
"When I put the specimens under the blue light (used for evoking fluorescence), every single amphioxus had a bright green area in the anterior that was fluorescent," said Deheyn.
Follow-on analyses in the Tampa specimens, along with similar species samples from France and Japan, revealed details of how the fluorescence spreads along the animal's body as well as how the animal fluoresces at different stages of development.
Amphioxus—also called a lancelet—is found primarily in coastal areas and lives mostly burrowed in ocean sand except for its head. Previous studies have shown it to be sensitive to changes in light exposure.
Deheyn says the exact role of amphioxus' fluorescence is not known. One hypothesis is that the proteins might be used as a form of "sunscreen," protecting the animal by absorbing harmful ultraviolet light and shielding it away as fluorescent light. GFPs also may play a role as protective antioxidants, decreasing stress levels undergone by cells when exposed to temperature fluctuations or other environmental changes.
Fluorescence has been used extensively in biotechnology, biomedicine, bioengineering and lately in nanotechnology. GFPs have been used as markers to examine gene expression as well as probes for tracking how molecules transfer energy.
"(GFP) is an easy protein to work with and to use as a label," said Deheyn, a scientist in the Marine Biology Research Division at Scripps. "It's easy to locate and stimulate so it has been used widely around the world. There is a great deal of interest in finding new fluorescent compounds and proteins that can show different characteristics of light production."
Deheyn's latest investigations focus on finding GFPs in animals in marine as well as terrestrial environments.
In addition to Deheyn and Holland, Biological Bulletin paper's coauthors include James McCarthy, Magali Porrachia and Greg Rouse of Scripps Oceanography, Kaoru Kubokawa of the University of Tokyo and Akio Murakami of Kobe University.
The study was funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research's Biomimetics, Biomaterials and Biointerfacial Sciences program and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Note to broadcast and cable producers: UC San Diego provides an on-campus satellite uplink facility for live or pre-recorded television interviews. Please phone or e-mail the media contact listed above to arrange an interview.
####
About University of California, San Diego
Scripps Institution of Oceanography, at UC San Diego, is one of the oldest, largest and most important centers for global science research and graduate training in the world. The National Research Council has ranked Scripps first in faculty quality among oceanography programs nationwide. Now in its second century of discovery, the scientific scope of the institution has grown to include biological, physical, chemical, geological, geophysical and atmospheric studies of the earth as a system. Hundreds of research programs covering a wide range of scientific areas are under way today in 65 countries. The institution has a staff of about 1,300, and annual expenditures of approximately $140 million from federal, state and private sources. Scripps operates one of the largest U.S. academic fleets with four oceanographic research ships and one research platform for worldwide exploration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mario Aguilera or Cindy Clark
858/534-3624;
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








