Home > Press > Imaging quantum entanglement
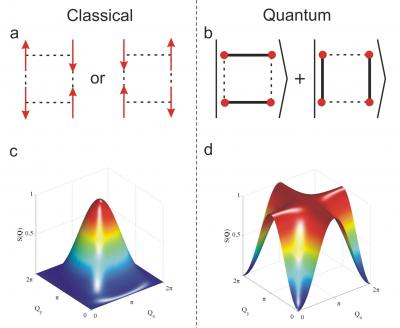 |
| For simplicity, the team focused on a square of spins, the tiny bar magnets associated with the electrons in the copper atoms in the organometallic material studied by the researchers. The left (c) shows a calculated neutron image for these spins when they behave as classical objects (a), while the right (d) shows the image when they are entangled (b). The images are dramatically different in the two cases, taking the form of a nearly circular spot for the classical case and a cross for the quantum, entangled state.
Credit: London Centre for Nanotechnology |
Abstract:
An international team including scientists from the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN) today publishes findings in the journal ‘Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences' (PNAS) demonstrating the dramatic effects of quantum mechanics in a simple magnet. The importance of the work lies in establishing how a conventional tool of material science - neutron beams produced at particle accelerators and nuclear reactors - can be used to produce images of the ghostly entangled states of the quantum world.
Imaging quantum entanglement
London, UK | Posted on September 21st, 2007At the nano scale, magnetism arises from atoms behaving like little magnets called ‘spins'. In ferromagnets - the kind that stick to fridge doors - all of these atomic magnets point in the same direction. In antiferromagnets, the spins were thought to spontaneously align themselves opposite to the adjacent spins, leaving the material magnetically neutral overall. The new research shows that this picture is not correct because it ignores the uncertainties of quantum mechanics. In particular, at odds with everyday intuition, the quantum-mechanical physical laws which operate on the nano-scale allow a spin to simultaneously point both up and down. At the same time, two spins can be linked such that even though it is impossible to know the direction of either by itself, they will always point in opposite directions - in which case they are ‘entangled'.
With their discovery, the researchers demonstrate that neutrons can detect entanglement, the key resource for quantum computing.
One of the lead authors of the work, Professor Des McMorrow from the LCN, comments: "When we embarked on this work, I think it is fair to say that none of us were expecting to see such gigantic effects produced by quantum entanglement in the material we were studying. We were following a hunch that this material might yield something important and we had the good sense to pursue it."
The researchers' next steps will be to pursue the implications for high temperature superconductors, materials carrying electrical currents with no heating and which bear remarkable similarities to the insulating antiferromagnets they have studied, and the design of quantum computers.
####
About University College London
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender, and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine. In the government’s most recent Research Assessment Exercise, 59 UCL departments achieved top ratings of 5* and 5, indicating research quality of international excellence.
UCL is the fourth-ranked UK university in the 2006 league table of the top 500 world universities produced by the Shanghai Jiao Tong University. UCL alumni include Mahatma Gandhi (Laws 1889, Indian political and spiritual leader); Jonathan Dimbleby (Philosophy 1969, writer and television presenter); Junichiro Koizumi (Economics 1969, Prime Minister of Japan); Lord Woolf (Laws 1954, Lord Chief Justice of England & Wales); Alexander Graham Bell (Phonetics 1860s, inventor of the telephone), and members of the band Coldplay.
About the London Centre for Nanotechnology
The London Centre for Nanotechnology is a joint enterprise between University College London and Imperial College London. In bringing together world-class infrastructure and leading nanotechnology research activities, the Centre aims to attain the critical mass to compete with the best facilities abroad. Furthermore by acting as a bridge between the biomedical, physical, chemical and engineering sciences the Centre will cross the 'chip-to-cell interface' - an essential step if the UK is to remain internationally competitive in biotechnology. Website: http://www.london-nano.ucl.ac.uk
About Imperial College London
Consistently rated in the top three UK university institutions, Imperial College London is a world leading science-based university whose reputation for excellence in teaching and research attracts students (11,000) and staff (6,000) of the highest international quality. Innovative research at the College explores the interface between science, medicine, engineering and management and delivers practical solutions that enhance the quality of life and the environment - underpinned by a dynamic enterprise culture. Website: http://www.imperial.ac.uk
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dave Weston
44-020-767-97678
mobile: +44 (0) 7733 307 596
out of hours +44 (0)7917 271 364
University College London
Copyright © University College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








